7 dangerous phishing attack methods you need to know about
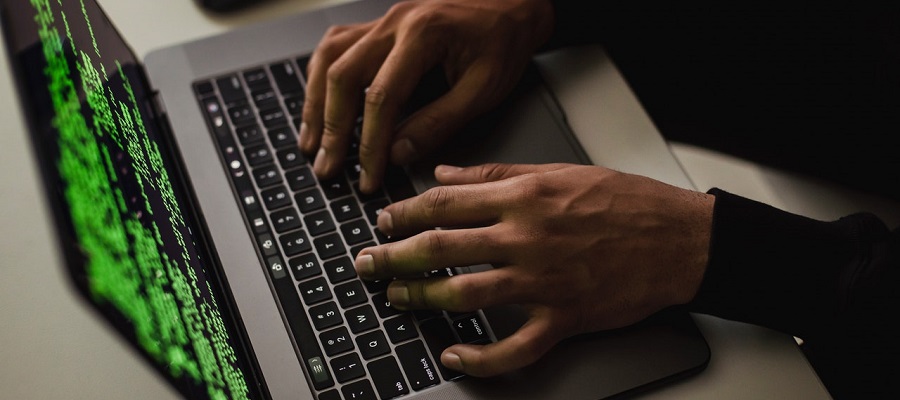

What Phishing Means - A Clear Definition
Phishing is one of the oldest methods of hacker attacks. The term has been doing the rounds since the 90s and probably comes from the word combination "fishing" and "password harvesting".
Hackers use a feigned respectability to try to harvest sensitive data from users via e-mails or websites. Such data can be various passwords, account data and personal information.
Imagine the following scenario: You receive a professional email that makes a serious and credible impression. Not only that, but the sender of the e-mail is your bank, complete with its logo. After all, you trust your bank. In this e-mail you are asked to click on a link. According to the e-mail, a technical fault has occurred at the bank. To ensure the security of your data, you have to enter and confirm your bank details again. Unfortunately, this is not your bank's website, but the website of the criminal. Consequently, your data could now be used for illegal purposes.
Most users are now aware of such attacks. Nevertheless, phishing attacks have increased dramatically in recent years. While users are becoming more sensitive, cyber attacks are becoming smarter and more sophisticated at the same time. The strategies and implementation of these attacks have never been more professional and personalized than they are today.
How phishing works - The most common methods
1. DECEPTIVE PHISHING
The most common form of a dangerous phishing attack method, which we have also highlighted in the example above. In this case, the attacker tries to obtain sensitive information. For example, he manages to do this via a fake email or website.

Source: tripwire.com
In doing so, the attacker pretends that the e-mail or website originates from a trustworthy organization. This unscrupulous pretense is a prerequisite for the entire strategy. Especially since bad German or mocked-up company logos are becoming increasingly rare in these emails.
The goal of the attack is to trigger a user action. Such an action may be clicking a link in the email. The victim may then be asked to update their user data or make a payment.
The more professional the email or target page looks, the greater the danger for the potential victim. The hackers try to create a sense of urgency or necessity in the same step.
Accordingly, it is more than advisable that you always keep an eye on URLs, sender address, email headers and spelling mistakes.
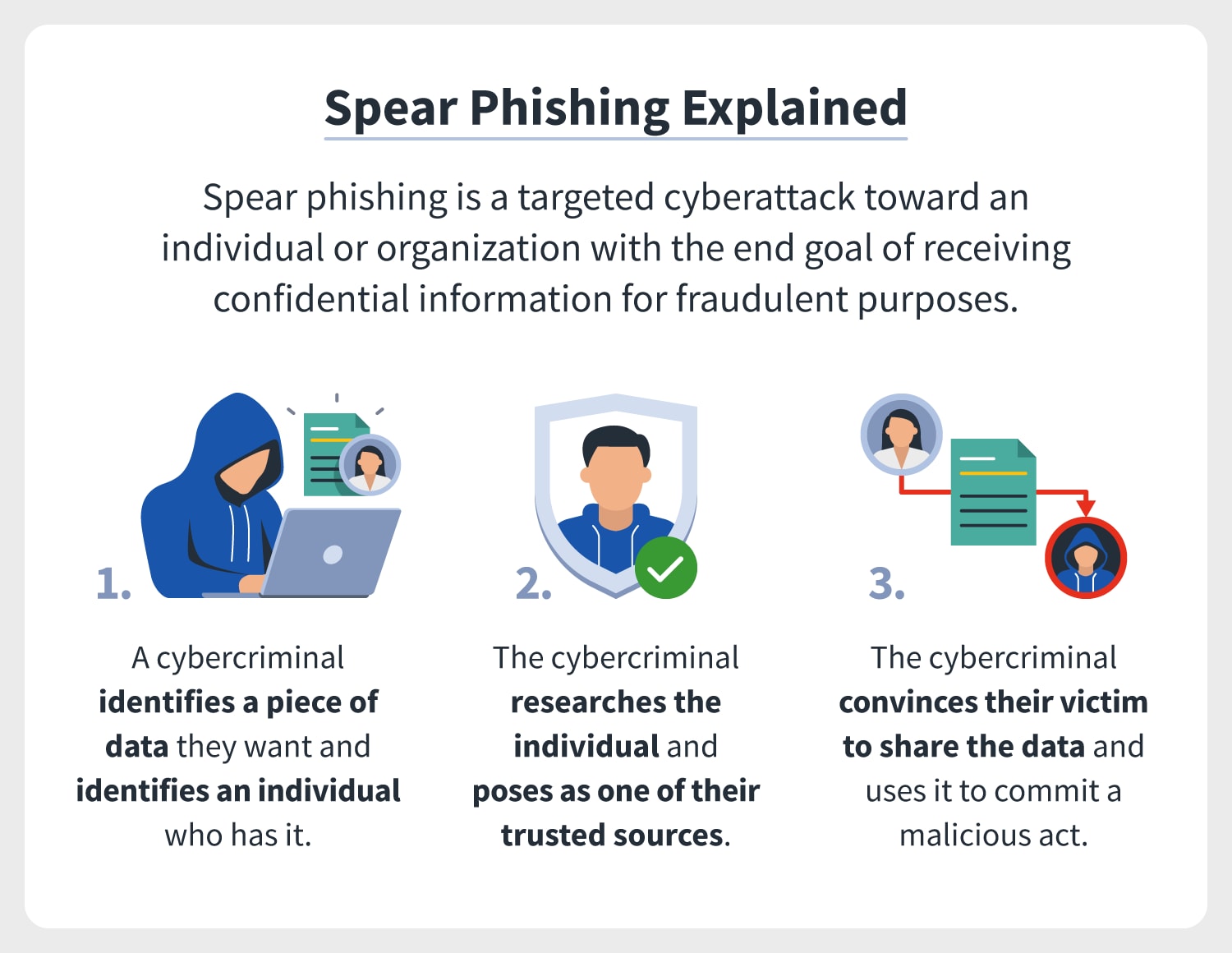
2. SPEAR PHISHING
Spear fishing (or spear phishing) is highly targeted, often personalized phishing attacks. Although this form of phishing shares similarities with deceptive phishing, this is an even more sophisticated attack variant.
Source: Norton
Once again, the sender pretends to be from a known, reliable source. However, the attacks look a bit more believable in this case.
By the way, such attackers often disguise themselves as employees of a business partner. In addition, they conduct research in advance on social media platforms about the target person or organization. This increases the chances that the hackers will "fish out" critical data from the people concerned.
A useful countermeasure is employee training that simulates a phishing attack. The Phish Threat training program from Sophos is such a meaningful security awareness training program. In this way, you also promote a strong security awareness culture in your company.
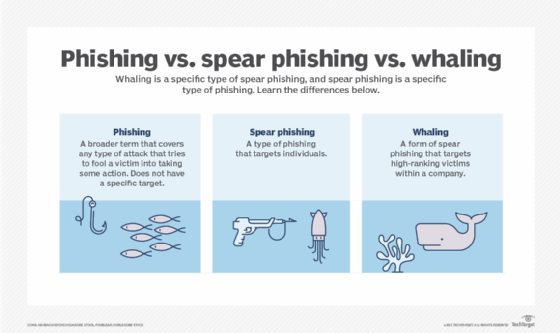
3. WHALING
In other words, the aim here is to catch a "big fish". Managing directors in particular are the focus of this phishing variant.
Source: techtarget.com
The first phase is once again to lure the affected executive. Once this has been achieved, the second phase of the attack is the CEO fraud. The term "business email compromise" (BEC) is also used for this.
Here, the hacker gains access to the personal e-mail account of a CEO. He pretends to be the CEO and is thus able to request information and make transactions via the stolen e-mail account.
This allows the fraudster to authorize wire transfers to an institution of his or her choice, for example. Whaling is particularly lucrative for criminals because executives are typically assigned the most access and approval rights.
You can counter the risks of a CEO fraud with multi-factor authentication (MFA) in financial accounting and customized IT security training for executives.
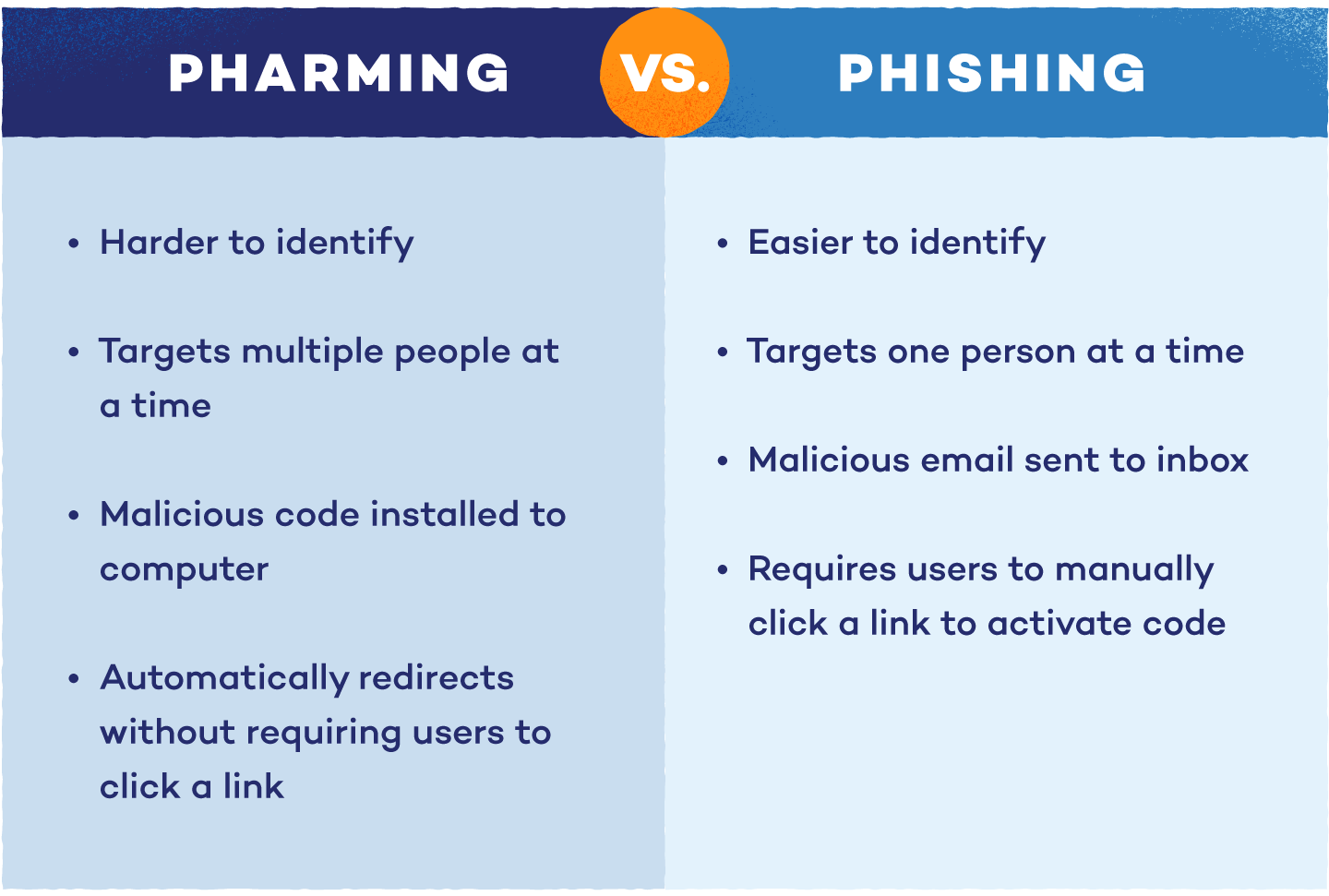
4. PHARMING
Source: pandasecurity.com
When the classic methods mentioned above fail, fraudsters turn the tables. They manage to do this by gaining access to the Domain Name System (DNS), for example. The DNS naming system uses DNS servers to translate website names, such as www.google.de, into IP addresses, such as 123.221.123.1.
In this case, a hacker or pharmer attacks a DNS server and changes the IP address associated with a website. Then, the hackers use this affected domain to redirect website visitors to the fake website of their choice. This redirection happens even though the affected visitors had actually entered the correct, website name. From this point on, there is a risk that the affected persons will disclose their bank details, for example.
For effective phishing protection, only visit encrypted (HTTPS) websites. You should also rely on a holistic IT security concept in your company that offers multi-layered and proactive protection for your systems.
5. DROPBOX PHISHING
Dropbox is a popular data storage platform and is used by businesses and individuals worldwide. Millions of people upload their personal data and share it with friends and colleagues. No wonder this service can have attack and success potential for fraudsters.
One dangerous phishing attack method is to obtain a user's access and account data via fraudulent emails that look almost identical to the original Dropbox emails.
Such a fake email could request a "security check" of a user profile, for example. But it could also make a shared document available for download.
6. GOOGLE DOCS PHISHING
Fraudsters prefer to specialize in several cases. For example, they focus on one provider, gain experience and become better and more dangerous. Analogous to Dropbox phishing, Google Drive phishing business can be extremely lucrative as well.
In several cases, Google Drive users received Google Docs document invitations via email a few years ago. Those who clicked on it shared their contacts and additionally left room for a malware infection of their computer. This was quite successful, because the target page was actually a Google Drive page. At first glance, the invitations actually appeared credible and unsuspicious.
7. CLONE PHISHING
In this method, an almost identical email is generated based on a genuine, legitimate email with an attachment. Then, the fraudster replaces the file attachments with malicious malware. As a result, the attacker creates a dangerous email clone. He then uses a similar email address as the regular sender and sends a second version of the real, initial email to the same recipient.
Such phishing campaigns are very dangerous because the hackers follow a very specific, customized approach. Victims of this attack assume that the second, malicious email is an update of the first, genuine email. Since they are already familiar with the content of the email, they tend to open the attached infected document much faster and carelessly.
Now you have learned 7 dangerous phishing attack methods. In the second part of our phishing post series, we will show you concrete signs of the attack methods described above. This will help you detect phishing attacks easier and faster.
How often have you had the suspicion that received emails were likely to be phishing? Are these dubious email messages becoming less or more frequent for you? Do you have any questions or suggestions in this regard? Feel free to leave a comment here or contact us directly. We look forward to your feedback!


